Lead
Joseph Rodriguez
Multi-Code GW Formation Channel Inference
Project Overview
This project develops a multi-code, physics-informed framework to infer the astrophysical formation channels of compact-object mergers observed in GWTC-4, while explicitly quantifying and diagnosing theoretical uncertainty in population-synthesis modeling. Using ensembles generated from independent stellar-evolution codes (COMPAS and COSMIC, with POSYDON planned), the pipeline applies realistic selection effects and simulation-based inference to recover posterior distributions over population hyperparameters and formation-channel fractions. Unlike single-model studies, this work treats cross-code disagreement as a first-class scientific object, mapping where and why simulators diverge in parameter, metallicity, and observable space. A domain-adaptation layer aligns simulated and observed events, and built-in falsification criteria flag regimes where simulator systematics dominate over observational information, rendering channel inference unreliable. The result is not just a set of inferred channel fractions, but a structured assessment of where current binary-evolution theory succeeds, fails, and must be refined to support robust gravitational-wave population inference.
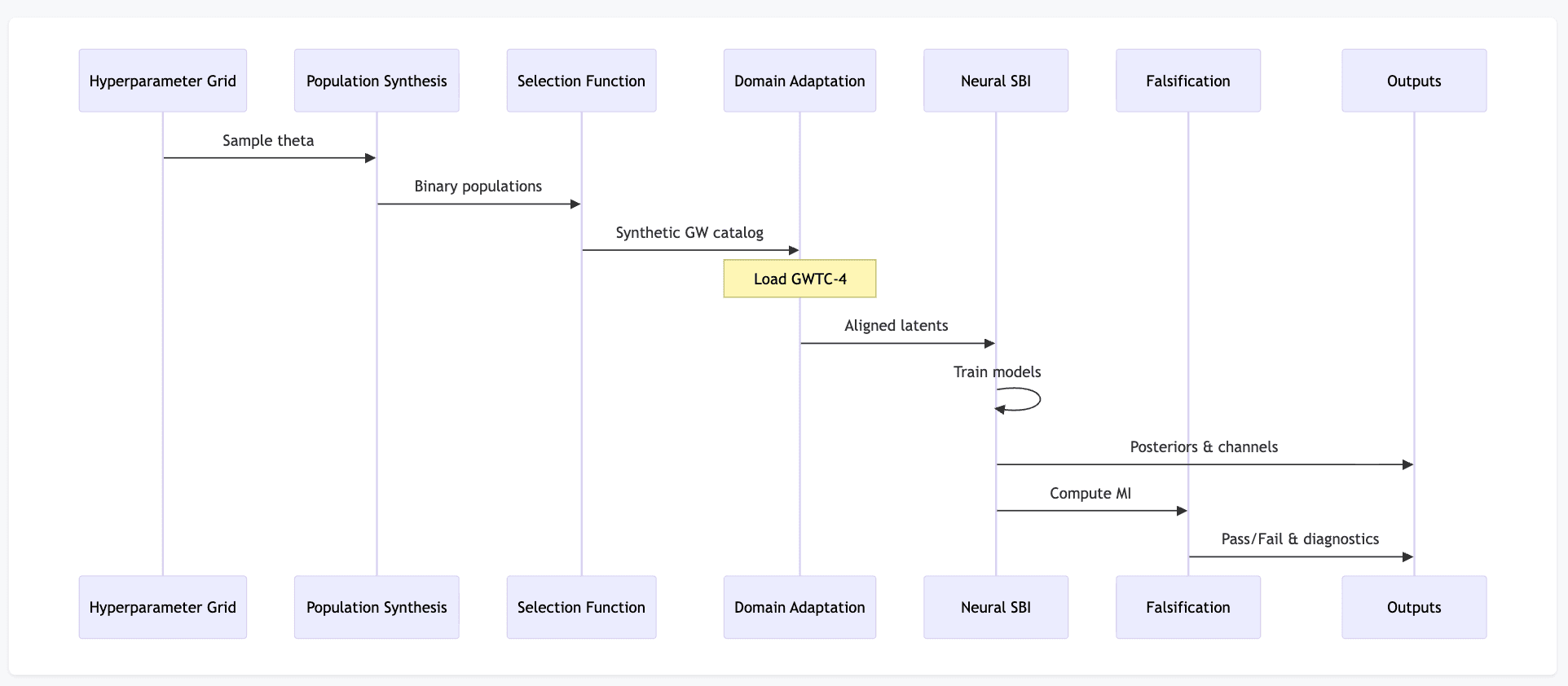
Data Flow Sequence
Scope of Work
Technical Details
Ensemble generation and standardization
Run COMPAS and COSMIC over matched sparse grids in key hyperparameters (e.g., common-envelope efficiency, natal kick dispersion, wind mass loss, metallicity), store outputs in a unified HDF5 schema, and tag each sample with simulator identity for downstream epistemic analysis.
Selection-function and observable construction
Convert source-frame populations to detector-frame observables by applying cosmology, metallicity-dependent formation rates, and catalog-level detectability criteria, producing simulated distributions in ( 𝑚 1 , 𝑚 2 , 𝜒 e f f , 𝑧 , 𝑝 d e t ) (m 1, m 2 , χ eff, z, p det).
Latent-space alignment and domain adaptation
Map simulated detections and GWTC-4 posterior samples into a shared latent space using learned encoders with distribution-matching losses (e.g., MMD and/or adversarial objectives) to reduce simulator–detector mismatch prior to inference.
Neural simulation-based inference and diagnostics
Train set-based neural density estimators (normalizing flows) on aligned populations to approximate 𝑝 ( 𝜃 ∣ G W T C - 4 ) p(θ∣GWTC-4), while computing mutual-information and code-identifiability metrics to quantify epistemic uncertainty and trigger falsification criteria.
